We have all encountered problems multiple times and more often than not, we have come up with ideas. The problem is in actualizing the ideas. This is where design thinking comes in. Design thinking can be applied to so many areas whether you want to solve a local problem or you are on the verge of launching a product.
Tim Brown, CEO of IDEO has a simple definition of design thinking. He defines it as a human-centred approach to innovation that draws from the designer’s toolkit to integrate the needs of people, the possibilities of technology, and the requirements for business success.
Design thinking is also defined as a non-linear, iterative process that teams use to understand users, challenge assumptions, redefine problems and create innovative solutions to prototype and test.
Design and Design Thinking
Design is solution-focused and action-oriented. It involves both analysis and imagination. Its purpose is to improve the quality of life for people.
Design thinking draws on logic, imagination, intuition, and systemic reasoning. It explores the possibilities of what could be and to create desired outcomes that benefit the user.
Design thinking is about using a process of diverging and converging to solve a wide range of problems while the design is making use of more elaborate and extensive activities of how a product should work.
Importance of Design Thinking
Design thinking allows you to look at problems and existing issues from a unique perspective.
Brainstorming and formulating ideas expands your knowledge.
Design thinking leads to collaboration which allows you to get feedback and results in creating a valuable experience for users.
Quality is assured due to rounds of testing of the minimal viable product.
Users' expectations are satisfied since they are actively involved in the development and design process.
Being involved in the design thinking process deepens your understanding of your users. As a result, you will understand the tools to be used and how to close gaps in the deliverables.
Design thinking allows us to think "outside the box" because as human beings, we develop patterns of thinking that are modelled on the repetitive activities and commonly accessed knowledge we surround ourselves with.
A quick story: a couple of years ago, there was an incident where a truck got stuck under a low bridge. It caused massive traffic and emergency personnel like firefighters, engineers, and other truck drivers gathered together to devise a plan on how to handle the situation. Each personnel suggested a solution based on their level of expertise. A young boy who witnessed the debate volunteered a solution of deflating the tires. Once they did, the truck was able to move through the low bridge. This story is symbolic of the struggles we face when the apparent solutions are hard to find due to self-imposed constraints we work within.
Design Thinking Process
As stated earlier design thinking is non-linear, therefore this process should not be thought of as hierarchical but as phases to an innovative project.
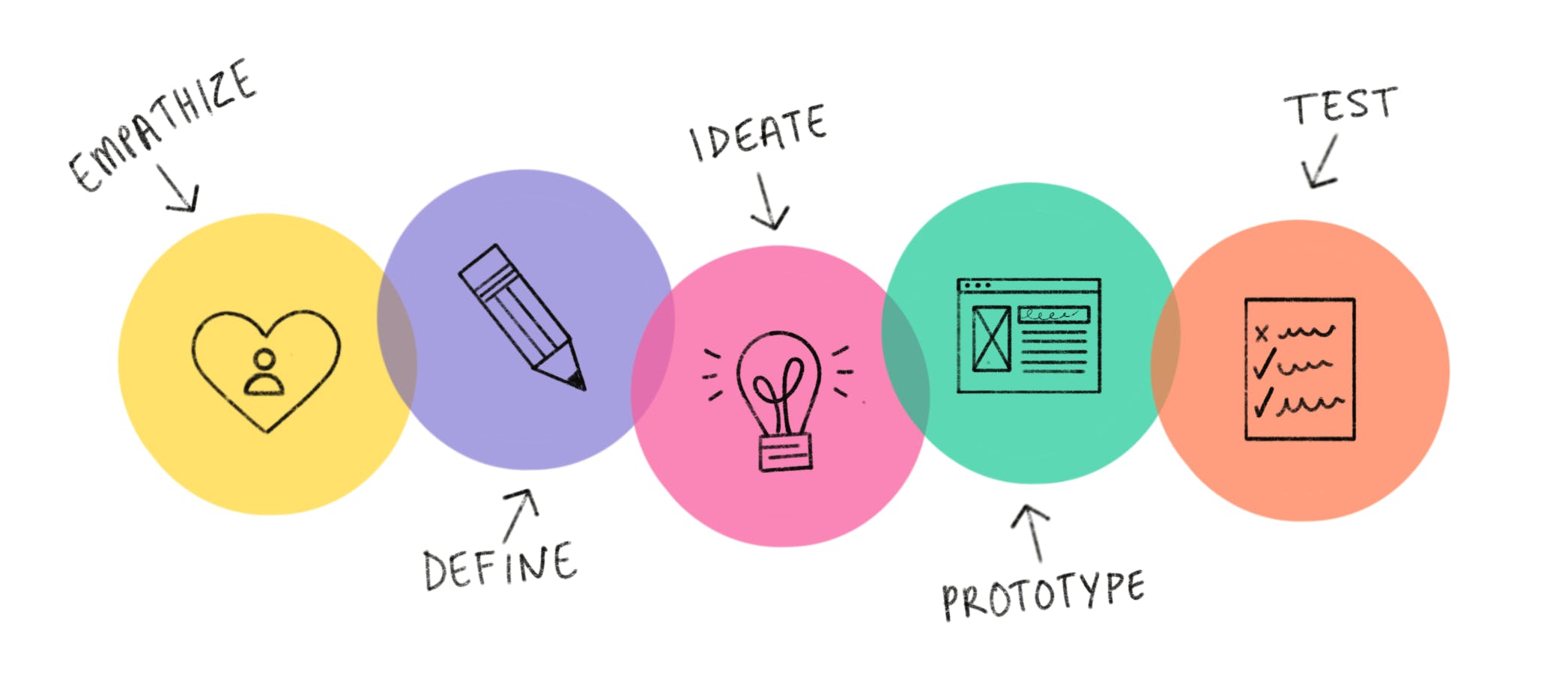
Design thinking has five phases:
- Empathize
- Define
- Ideate
- Prototype
- Test
Empathize
Empathize is the act of understanding the user's perspective. This step is vital because it allows you to set aside your assumptions and get insights into the end-users needs. You gain an empathetic understanding typically through user research.
Define

The definition stage is where you analyze your observations and define the problem. The definitions are normally called problem statements. We can develop personas by asking questions like:
- What are the user's demographics?
- What is the user's background?
- How do they communicate?
- What is their goal?
- What challenges are they experiencing?
Through these questions, you get to keep the process human-centred.
Ideate

This phase involves developing and generating as many ideas as possible. This can be done through divergent and convergent thinking.
Divergent thinking involves looking for different ways to view the problem through brainstorming while convergent thinking involves selecting the best idea out of other innovative ideas to follow through with.
Prototype
 This is an experimental phase, whose aim is to identify the best possible solution for each of the problems found. Prototypes are representations of how the final product would look like.
This is an experimental phase, whose aim is to identify the best possible solution for each of the problems found. Prototypes are representations of how the final product would look like.
There are different types of prototyping but the main ones are low fidelity and medium fidelity.
Low fidelity can easily be sketched through pen and paper and you can easily get feedback from users on a real-time basis while implementing the changes within minutes. On the other hand, Medium fidelity is presented using storyboards and user scenarios. They are more functional when compared to low fidelity. Medium Fidelity Prototypes are the intermediate stages of product development.
Low fidelity is highly recommended for confirming the validity of your ideas.
Testing
 Testing is the last phase, where prototypes are vigorously tested.
This is often after making iterations, alterations, and refinements. You can use the results to redefine one or more problems to find or rule out alternative solutions.
Testing is the last phase, where prototypes are vigorously tested.
This is often after making iterations, alterations, and refinements. You can use the results to redefine one or more problems to find or rule out alternative solutions.
Critical Success Factors To Implementing Design Thinking
Leadership: Design thinking should be linked to the strategic goals of the organization to provide direction, resources, and commitment.
People: Enable champions of the organization to lead the change through lighthouse projects, in addition to building an internal design thinking community where best practices are shared.
Process: Evolve the design thinking process to include tools and methods to support the organization's objectives.
Environment: Create and develop collaborative workspaces for your workforce. Also, co-innovate with your clients and partners.
Design thinking works because it is a collaborative, co-creative process grounded in engagement, dialogue, and learning. Involvement of stakeholders during the problem definition and in developing solutions give you a better chance of gaining commitment for change and getting buy-in for your innovation.
Conclusion
In this article, we explored the concept and processes involved in Design Thinking.
To get more insights especially on matters regarding the persona on design thinking you can check out a webinar we held on design thinking here
This article was written by Velda Kiara

